09: Political Transitions
1490s and political transition
Transition: end of the “classic” Florentine republic
Machiavelli writes, lives amidst this era
New stability: mid 16th c
How (and why) should we follow a complicated and messy political story?
- multigenerational story
- many participants: many individuals, many states
- Alliances change quickly
- many different goals that may change as the situation changes
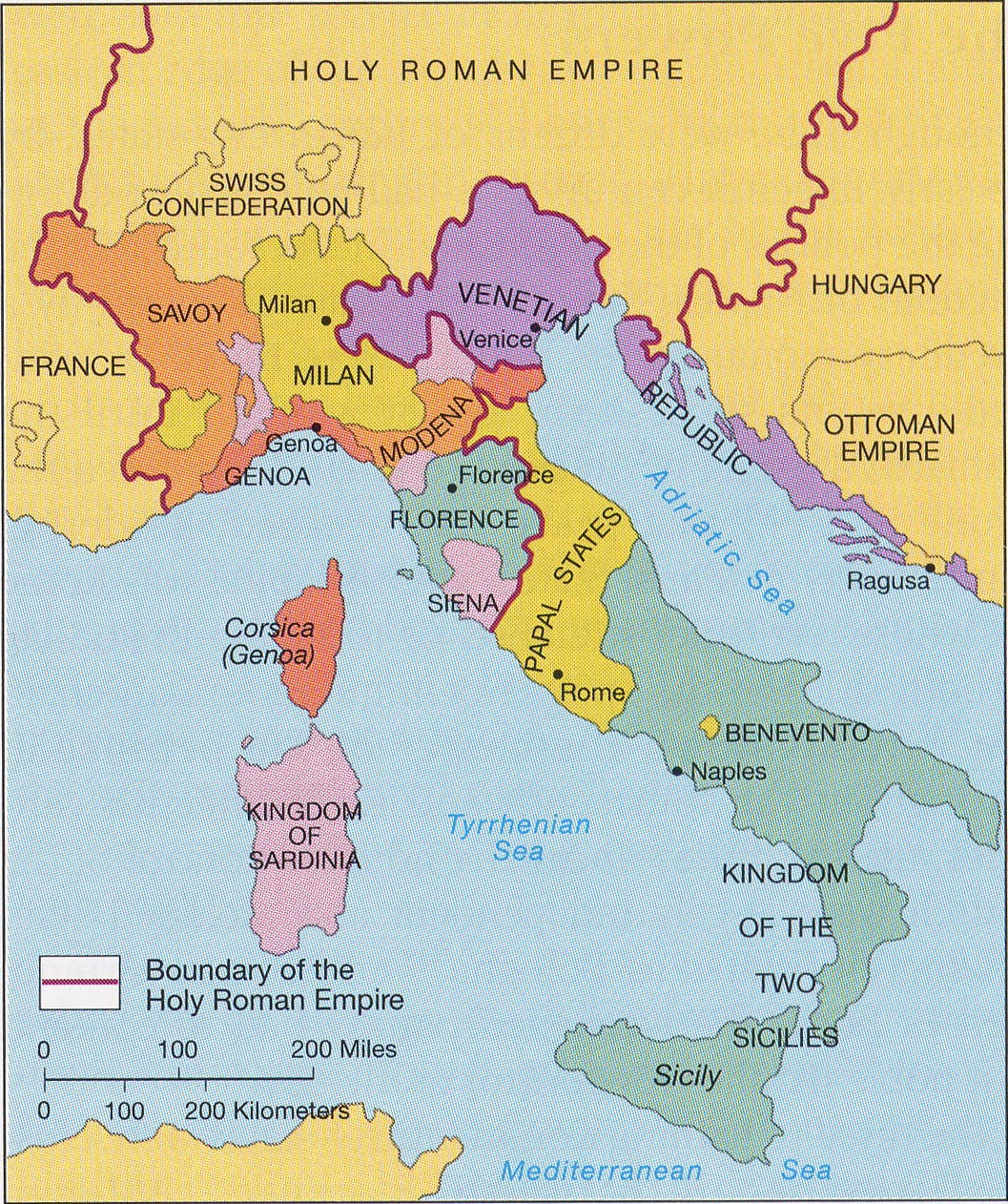
1494
From Lodi to Wars of Italy
“Italian League” treaty at Lodi, 1454.
recognize status quo, not to wage war, declare peace, or enter into alliances without others; military support; 25 years, renewable
“big 5” Florence, Venice, Rome, Milan, Naples
Little infrastructure
weakness after 1490
Big 5 and their situations ca 1494:
Kingdom of Naples (with Sicily); “Regno”
- Aragonese; Angevins before 1435
- End of Aragonese line
Papal States
- Rome de facto run by popes; regional representatives to subject cities
- Alexander VI (Rodrigo Borgia) 1492-1503
Venice
- stable oligarchy
- threats from Turkish expansion
Milan
Signorial government under Sforza, then Visconti
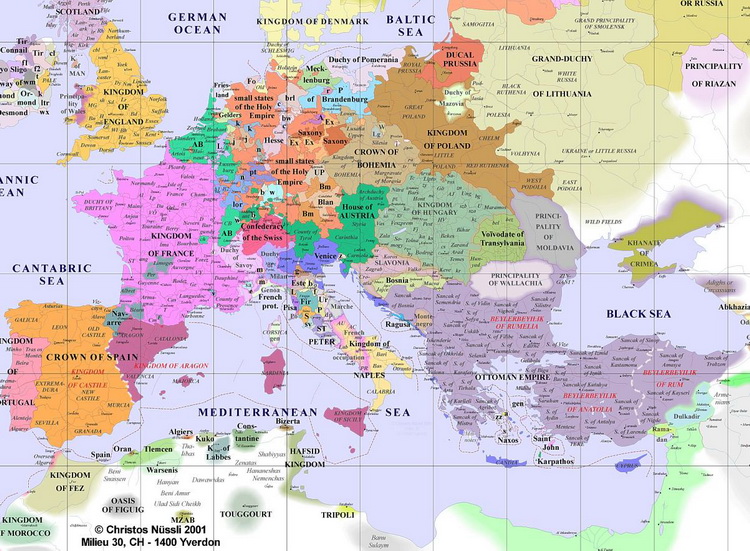 1500
1500
French Invasion 1494
Rise of European Kingdoms; outsize city-states
- Instability in Milan
- Child heir (Gian Galeazzo Sforza) with guardian (Ludovico il Moro); G-G now adult
- Charles VIII’s army Sept. 1494: to Naples
- Pope Alexander VI organizes “Holy League”
Papacy, Venice, Milan, Emperor Maximilian, K of Aragon
Second Wave:
Louis XII of France (1498-1515)
- 1499 Renews claims on Milan
- negotiates for Regno with Alexander VI
Julius II (1503-13) (Raphael, portrait,1511. London, Nat’l Gallery)
- 1505-06 campaign to recover old papal lands
1508 League of Cambrai. (against Venice): Rome, France, HRE, Mantua, Ferrara, Aragon (until 1509) Battle of Agnadello
Future Charles V (King of Spain 1516; HRE 1519
land route between Spain, Regno
1512 Medici return to Florence
Events in Florence
Map: Florence and contado 1494
1492: death of Lorenzo de’ Medici dies. Son Piero “succeeds”
1494: Piero negotiates badly with French
1494-1512 republican government
- Piero Soderini Gonfaloniere for Life 1502-12
- Great Council, ca 3000 members

- Savonarola
- Alliance with French
- Ottimati
- Piagnoni vs Arrabbiati; Savonarola burned 1498
- 1512 Papacy, Habsburgs agree to restore Medici in return for support: siege
1513 Giovanni di Lorenzo elected as Leo X (d. 1521)
Cousin Giulio made Archbishop of Florence, cardinal
1523-34 Giulio elected Clement VII (1523–34). We will return to them
Third Wave: Francis I and Charles V
1515 French retake Milan
1516 Charles inherits Spanish crown, 1519 HRE
1525: French lose to Imperial forces
Milan: Francesco Sforza under Hapsburgs 1525-35; then viceroy under Charles V
(Titian and shop: Francesco II Sforza)
1527 Sack of Rome
–In Florence: Medici rule overturned, republic 1527-30
1530 siege by Spanish Habsburg army, Medici returned (Duke Alessandro, 1530-37)
1529 treaties (Barcelona, Cambrai):
Spanish: Naples, Milan
1552 Cosimo I takes Siena 1554-55
1559 Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis
From this point, a period of relative stability
Some features of transition:
- Florence’s political context is now Europe-wide
- Florentines are no longer the sole decision-makers about the city’s future from 1512 onward
- big families (especially Medici) need to build their fortunes across Europe
- Local Florentines remain divided on the best type of government

