04 Political Organization and Courts
Introductory points
- Our chronological span: ca 1300-1600. Today: ca 1300
- Orientation: what is the political world ca 1300?
Europe’s political units
- kingdoms
- Holy Roman Empire
- City-states
- Other
Kingdoms: 14th c
Exx: England, France; Naples
kingship: hereditary BUT may include election
Nobles
Income
-
- a. lands that the king holds directly
- b. services (or cash equivalent) provided by nobles
- c. taxes
- d. income from courts, etc
- e. less income than we expect to see now
sources of tension
England:
ties to France
Barons and the king

Beaumaris Castle, Wales (Anglesey)
Economy
subsistence agriculture
commodity agriculture (wool)
peasants
London
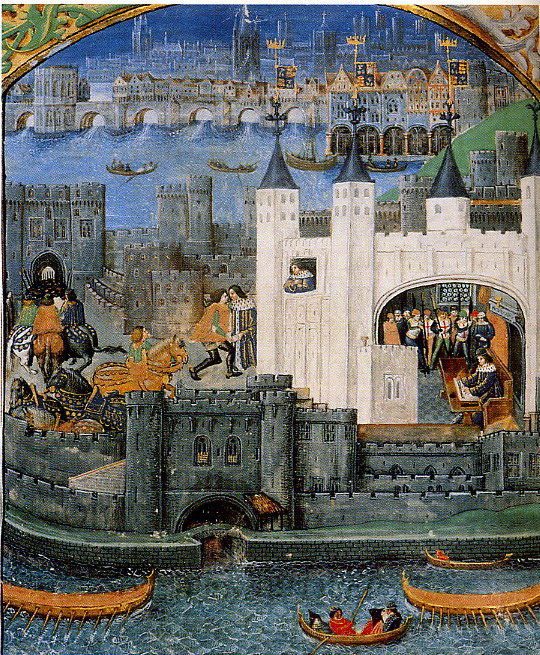

London, Tower and Bridge, 14th c (British Library)
France

The king and his nobles
The Holy Roman Empire: Central Europe
Definitions and origins
heirs of W. Roman empire established by Charlemagne
Several parts to imperial identity
a. Emperor is Lord over many smaller groups & tribes
b. Lord over Regions that included old W. imperial holdings
legitimacy
a. elected to kingships
b. crowned by pope
— Donation of Constantine
Trends and developments: what centralizes? — small internal units
Basic features:
Emperor, chancery, Diet (Reichstag), small court
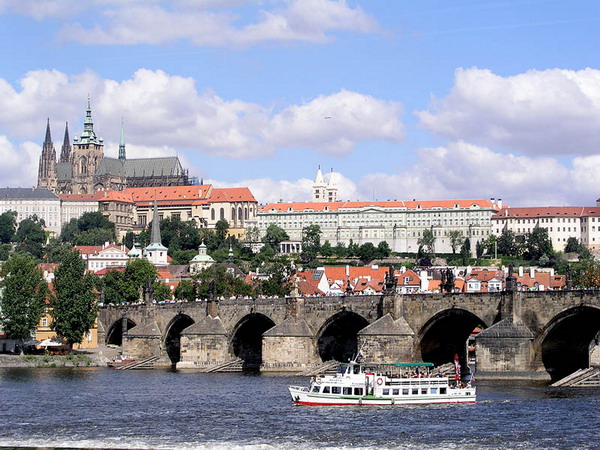

Prague Castle and Charles Bridge (begun 1357)
Italian politics
Regional variation
Economic, cultural dominance
3 big regions: N./Central Italy; Papal States; Kingdom of Naples
Northern/Central Italy
- terms: contado; signore
2. Major cities: Genoa, Milan, Venice, Florence
3. Economy
trade: Mediterranean to Europe
industry: textile production
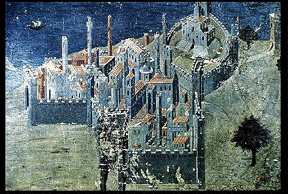
Ambrogio Lorenzetti, ca 1328
Central Italy: Papal States
Pope’s dual role

Southern Italy; Naples and Sicily
13th c, first half: Home of Emperor
13th c, second half: succession wars
by 1300: distinct from HRE
Kingdom: papal legitimacy

Robert of Anjou ( 1278-1343) King of Naples, from a Prato ms to Robert, British Library
Court Culture and Chivalry
11th c:
- the educated, virtuous prince-bishop
morality and fighting - technology innovation: stirrup: rise of horse-mounted fighting
Knighthood
Crusades (First Crusade 1096-99; Urban II)
Court Literature: Epic, Romance, Lyric
Jousts and Tournaments: Ritual and Entertainment

Tristan BL Add MS 5474 fol. 9r
Courts of southern France, former Carolingian regions
Southern French. (langue d’oc, Provencal)
ex: William IX of Aquitaine (1071-1127)
itinerant singers
Lover as feudal lord, beloved lady
Love as refinement
Love of God as comparison
Genres: Romance, chanson de geste
Exx: Song of Roland; Arthurian legend
