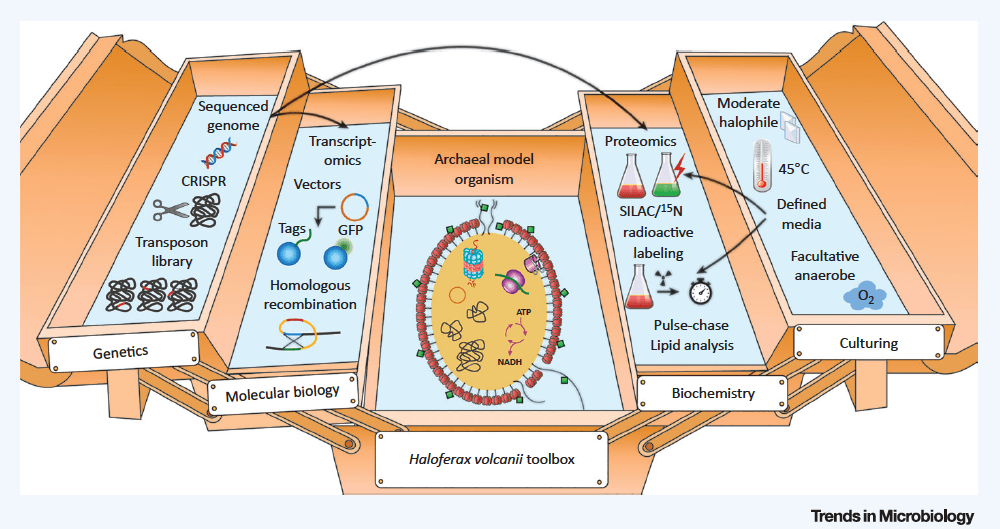
H. volcanii has emerged as an
important archaeal model system. An extensive repertoire of genetic, molecular biological, and biochemical
tools has been developed for this fast-growing, easily cultivated haloarchaeon, including expression vectors and
gene-deletion strategies, including CRISPR. Its low mutation rate and ability to grow on defined media allow
straightforward application of methods such as metabolic labeling, and the sequenced genome laid the
foundation for transcriptomics and proteomics studies.
Screen Shot 2018-11-19 at 8.05.13 PM-2mmegui
November 19, 2018 | 0 comments